Nitinol: The Transformative Material Reshaping the Medical Device Industry
In the MedTech industry, few materials have sparked as much interest and application as nitinol. Known for its unique properties of shape memory and superelasticity, nitinol (Nickel Titanium) is a shape memory alloy that has revolutionized the medical device industry . In simple terms, this means that nitinol can be set to a specific shape but will retain its shape even after being deformed.
What is Nitinol, and What is it Made Of?
Nitinol is a shape memory alloy composed of approximately equal parts nickel and titanium. These two elements are combined to create a metal with remarkable properties not found in any other material. The nitinol alloy’s material properties and therefore the part performance can be changed by the way the nitinol is processed, which is why there is so much more to processing nitinol than meets the eye. The fact that it can be shaped into an endless number of shapes enables its use across various applications.
How Does Nitinol Work?
Nitinol’s superiority lies in its ability to be set into a predetermined shape and then remember that shape. A primary property of interest is the transformation temperature. When deformed at lower temperatures, it can return to its original shape when heated above its transformation temperature . The transformation temperature is the temperature in which the nitinol returns to the shape that was set by heat treating it can be adjusted up or down by processing. This shape memory effect, coupled with nitinol’s ability to undergo significant deformation without permanent damage (superelasticity), makes it an invaluable asset in developing medical devices.
Biocompatibility of Nitinol Alloy as an Implant Material
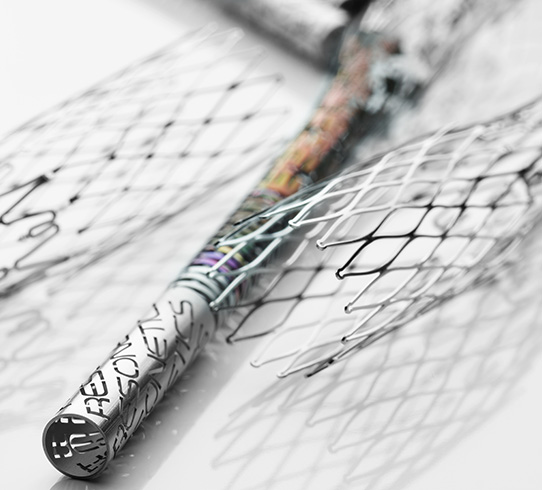
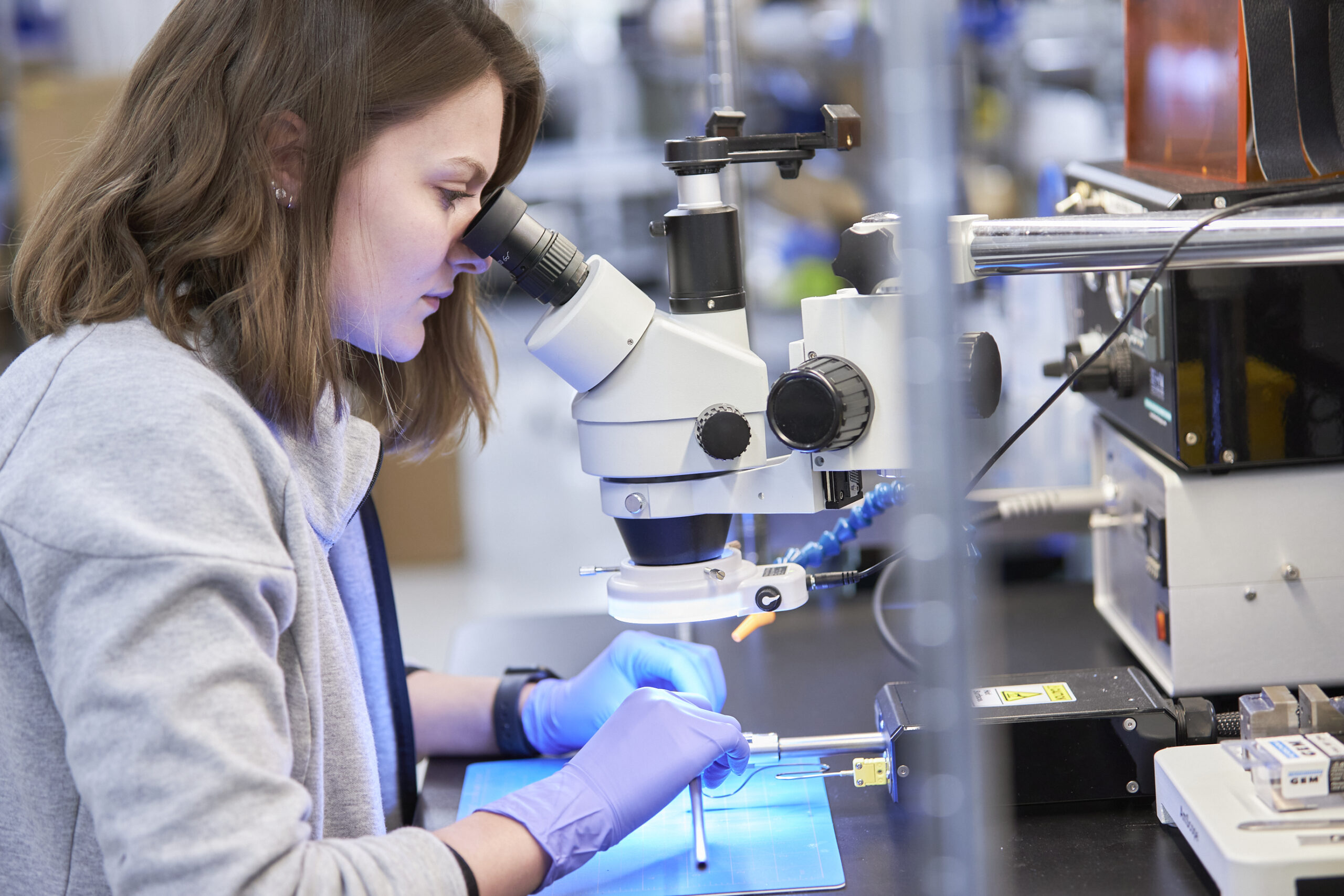
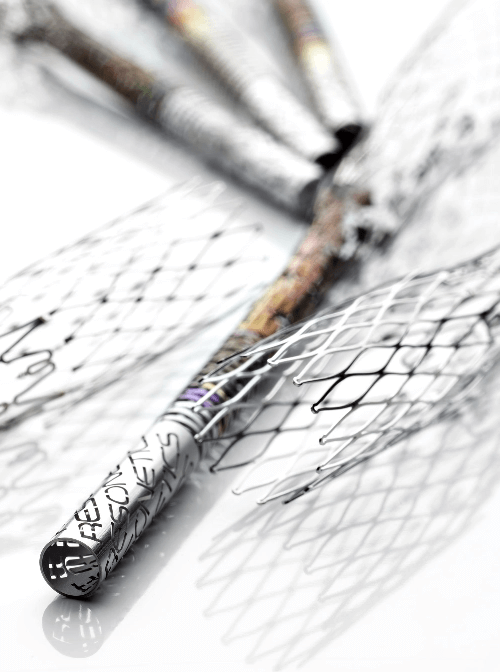
One of nitinol’s most crucial properties for medical applications is its biocompatibility. When electropolished and used as an implant material, nitinol poses minimal risk of adverse reactions, making it ideal for long-term implants. This compatibility, along with its corrosion resistance, ensures that nitinol-based devices can safely remain within the human body for extended periods of time.
Applications of Nitinol in the Medical Device Industry
Nitinol’s unique properties have led to its widespread and growing adoption in the medical field. For example, nitinol is used in a wide range of implants, from tiny neurovascular stents used in the brain to large nitinol heart valve frames that are used to replace the native valves in the heart that must be able to withstand millions of deformations as the heart beats. Nitinol is used in orthopedic applications like bone staples, and dental applications like flexible dental drills that bend but resist breaking. Nitinol is used in delivery systems because it offers both flexibility and kink resistance unlike traditional stainless-steel applications. New uses are being imagined daily which are transforming patient care and surgical outcomes.
Nitinol’s journey from a laboratory curiosity to a cornerstone of medical device innovation is a testament to its unique properties and the visionary work of researchers and engineers. As the medical device industry continues to evolve, nitinol’s role is set to grow, underpinning the next generation of medical innovations that will improve patient outcomes and healthcare efficacy.
Whether you’re at the forefront of medical device development or exploring the potential of nitinol for the first time, embracing this remarkable material could be the key to unlocking new possibilities in medical technology.