Laser Ablating
We have developed proprietary processes that use high-speed lasers to selectively remove material from a substrate or 3D machine micro-scale components and devices from a solid material. These processes minimize heat input, reduce thermal damage, and can be done in one setup, reducing handling and cost. Our Lightspeed Lab process experts can help you take advantage of these advanced technologies with industry-leading prototype solutions, design feedback, and manufacturing process development.
Our Technology
At Resonetics, we use state-of-the-art laser systems equipped with excimer and ultra-short pulse lasers that provide exceptional control over beam intensity, duration, and heat output. This ensures the highest quality of work with minimal thermal damage to the materials.
Our specialties include but are not limited to:
- Ablation depth control for blank (not through) vias or other features
- Selective material removal (remove top layers of material without damaging the materials underneath)
- 3D feature processing
- Multilumen processing with dynamic OD control
- Reel-to-reel wire coating stripping
- Profile control micro-via array drilling
3D Laser Machining
Our 3D laser machining process uses an ultra-short pulse laser to selectively remove material to produce cutting-edge micro-scale components that are too small for other processing methods. We design and build our own laser ablation systems that are fully automated, including in-process inspection and minimizing material handling.
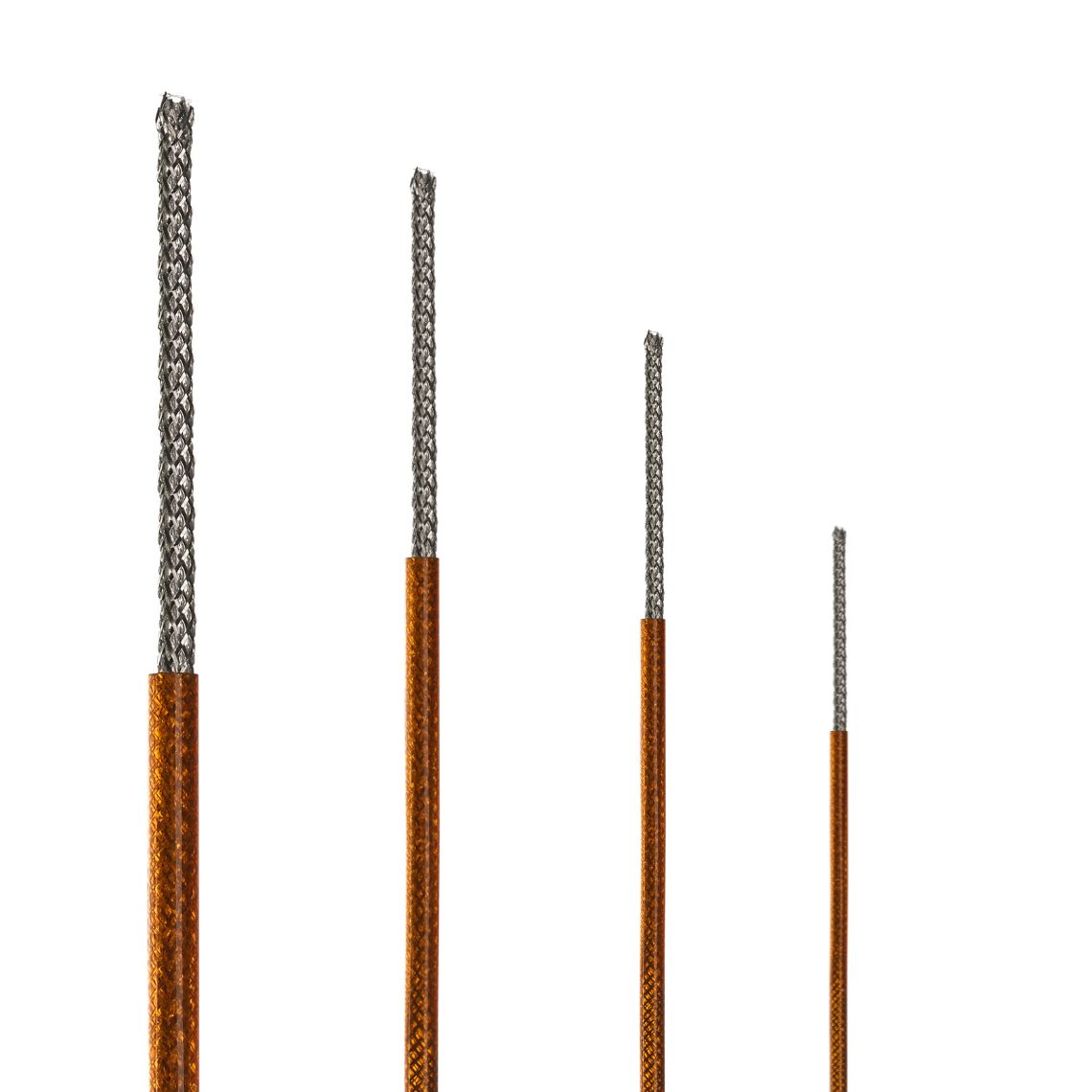

ASSURE Endpoint Detection
ASSURE Endpoint Detection is a patented process we developed for our custom reel-to-reel wire ablation platform. It solves a common challenge of removing multi-layer eccentric coatings from wires by using a closed-loop detector to adjust the laser ablation process in real-time, accommodating local inconsistencies in coating thickness. This allows our process to achieve a more consistent material removal, resulting in a more precise finished component.
Laser Ablation Applications
Laser ablation removes material for micromachining and fabrication applications such as:
- 3D micro components
- Wire coating stripping
- Radiopaque marker bands
- Single-lumen catheters
- Multi-lumen catheters
- Tip shaping of catheters
- Electrode coating removal
- Balloon surface texturing
Laser Ablating Materials
We perform laser ablation on a variety of materials, including, but not limited to:
- Polymers
- Polyamide
- Polyimide
- PEEK
- Nylon
- Pebax
- Metals
- Nitinol
- Stainless steel
- Titanium
- Tungsten
- Glass
Advantages of Polymer Laser Ablation
- Precision and Accuracy: Laser ablation allows for extremely precise cuts with clean edges, reducing the need for post-processing
- Versatility: This technique can be used on a variety of polymers, including sensitive and flexible materials
- Non-Contact Process: Since the laser does not physically touch the material, there is no mechanical wear and tear, resulting in better product longevity
- Customization: Laser parameters can be easily adjusted to meet specific requirements, allowing for broad customization of the ablation process
- Material Flexibility: In addition to polymers, laser ablation can be effectively applied to metals and glass, offering a comprehensive solution for diverse manufacturing needs